Structure of a leaf
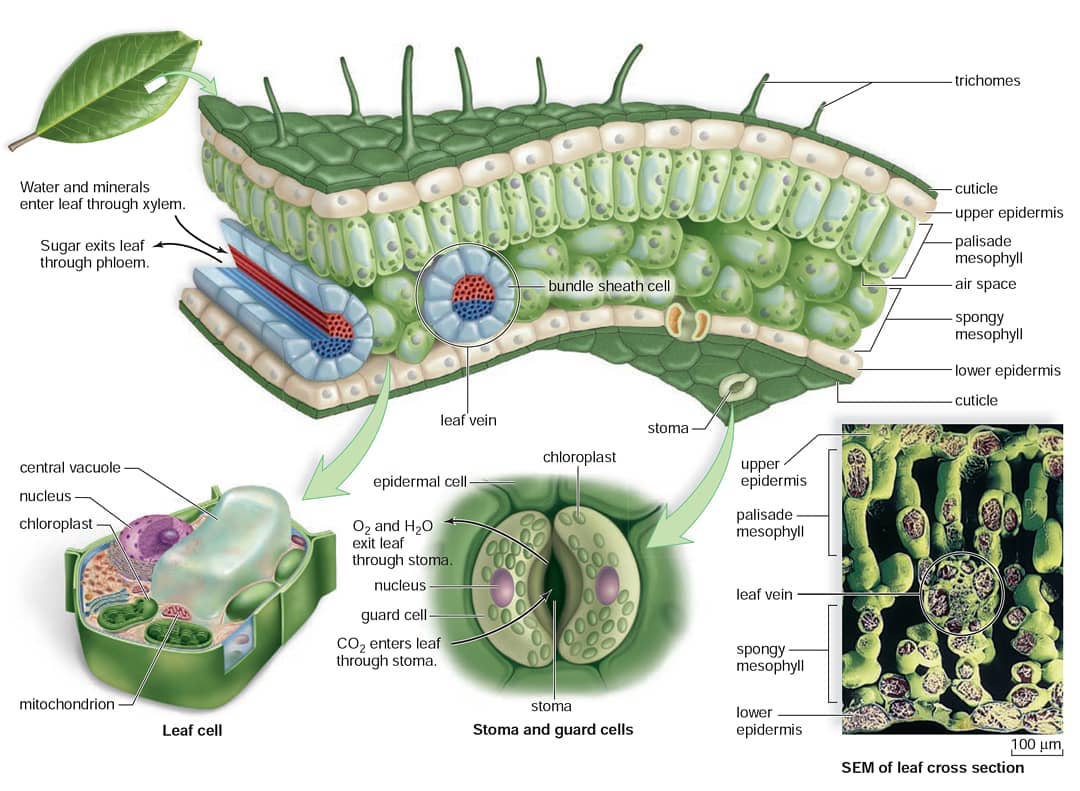
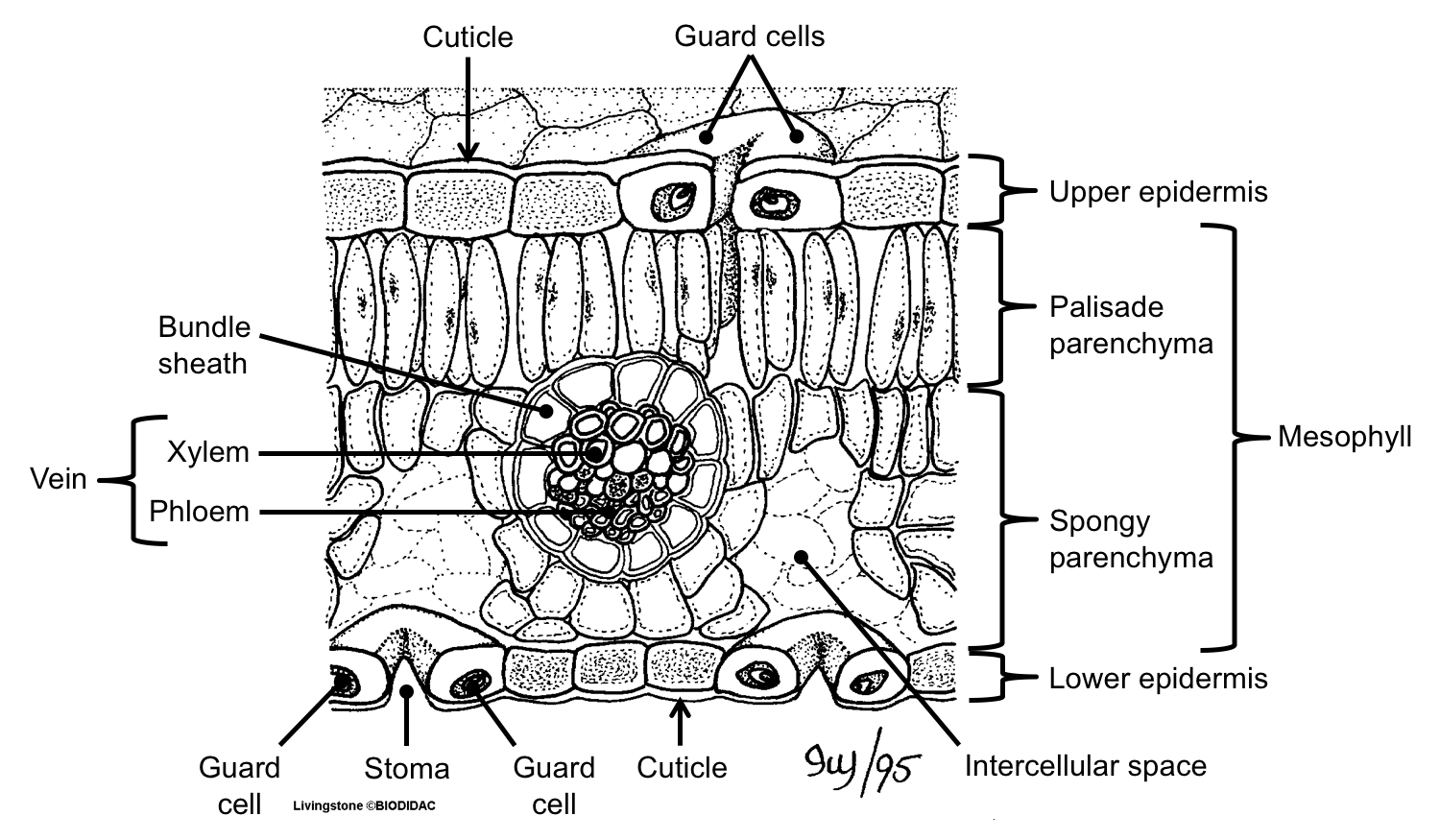
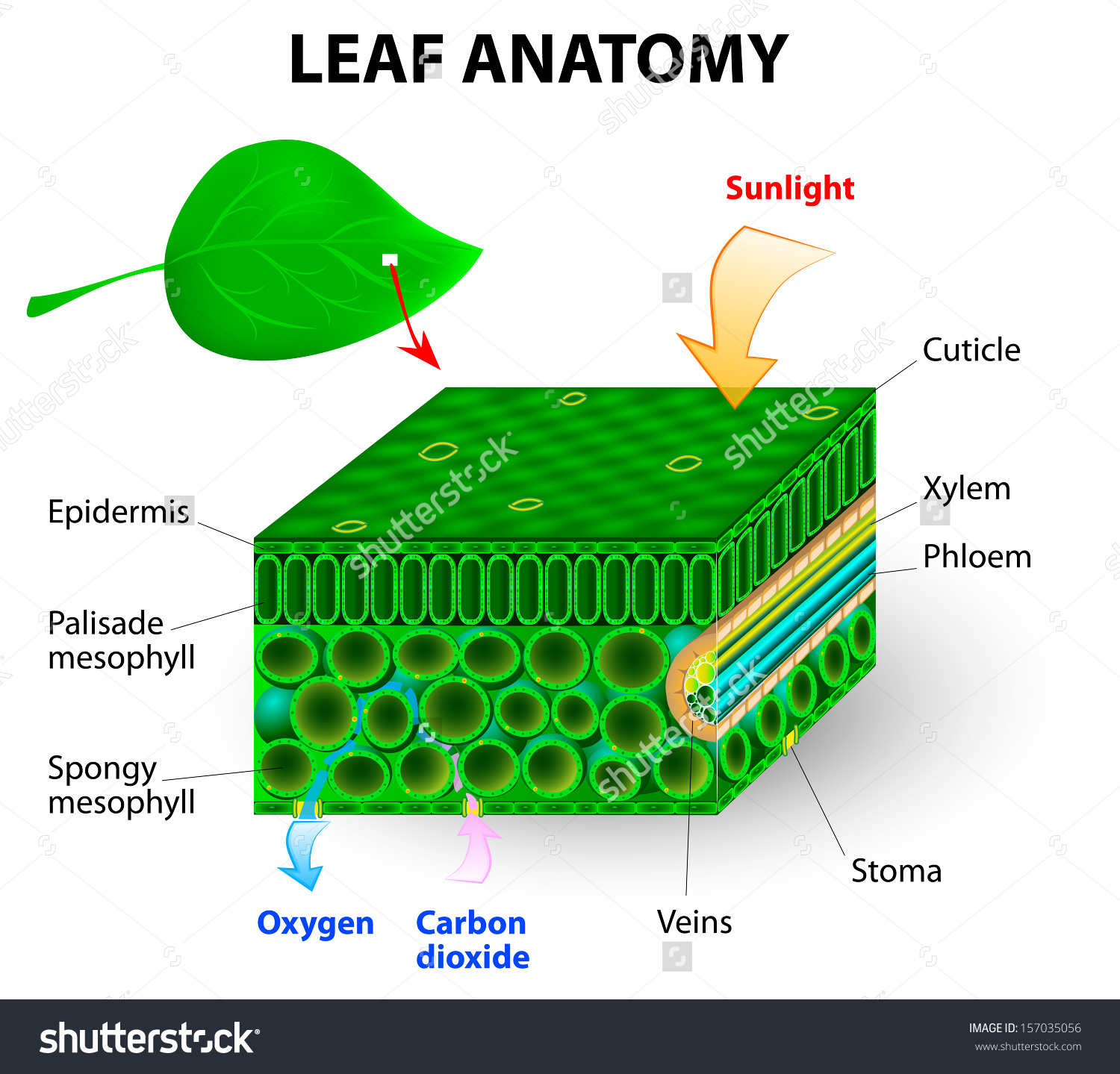
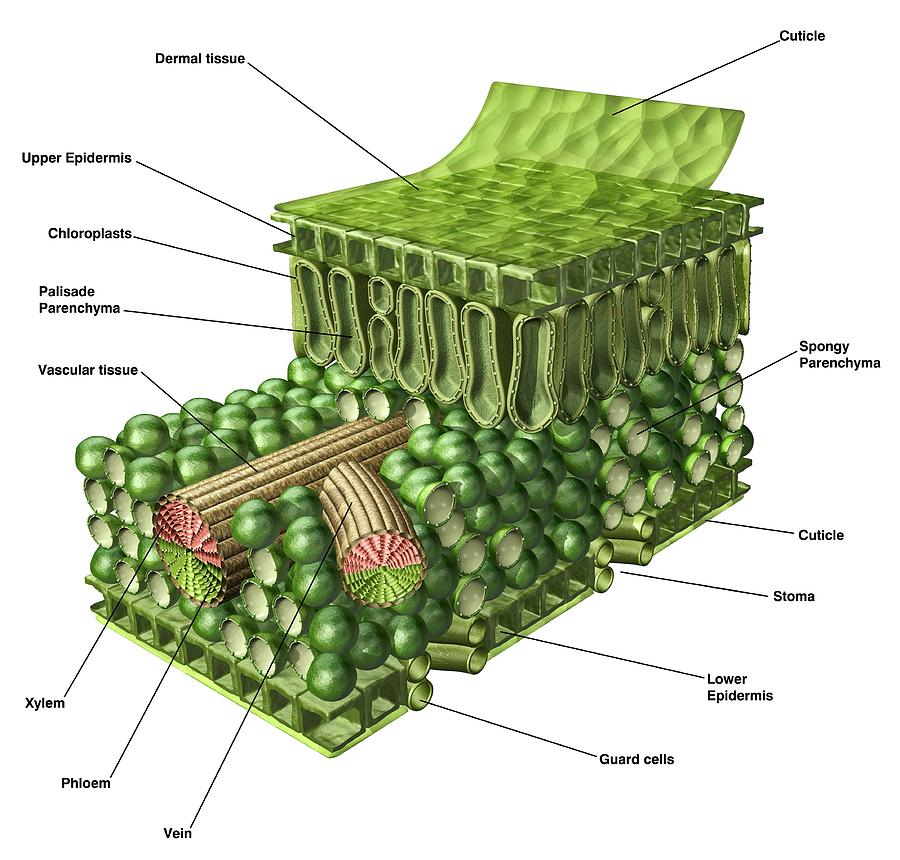
Like the stem, the leaf contains vascular bundles composed of xylem and phloem (Figure 3.4.2.6 − 7 3.4.2. 6 − 7 ). When a typical stem vascular bundle (which has xylem internal to the phloem) enters the leaf, xylem usually faces upwards, whereas phloem faces downwards. The conducting cells of the xylem (tracheids and vessel elements.

Leaf Labelled Stock Photo Download Image Now iStock
The table below describes the different structures in a leaf and their functions; Leaf Structures Table. Diagram showing the cross-section of a leaf. The specialised cells in leaves have adaptive features which allow them to carry out a particular function in the plant;. 6.2.3 Structure of the Leaf; 6.2.4 Living in Extreme Conditions;

Ts Of Dicot Leaf Diagram Amyhj
The structure of the umbrella tree leaf is typical of leaves in general (Above left photo). It has an outer layer, the epidermis, which produces a waxy waterproof coating. The epidermis of the undersurface produces guard cells, which swell and shrink to close and open the pores (stomata) which control the loss of water vapor (transpiration) and.
Leaf Structure & Evolution Digital Atlas of Ancient Life
The air space found between the spongy parenchyma cells allows gaseous exchange between the leaf and the outside atmosphere through the stomata. In aquatic plants, the intercellular spaces in the spongy parenchyma help the leaf float. Both layers of the mesophyll contain many chloroplasts. Figure 30.10. 1: Mesophyll: (a) (top) The central.

Leaf Structure photo Botany, Teaching biology, Biology
The palisade mesophyll cells are packed tightly together near the top of the leaf to collect as much sunlight as possible. They contain many chloroplasts and most photosynthesis takes place in these cells. The spongy mesophyll cells contain air spaces to allow the movement of gases (i.e. carbon dioxide and oxygen) throughout the leaf. The guard.

Parts of a leaf diagram. Preschool & PreK Science/Sensory
Parts of a Leaf Diagram 1. Petiole It is the stalk that connects a leaf to the stem of the plant, it is made of complex conducting tissues called vascular tissues. Functions Providing support to the leaf and keeps it erect Transporting water and nutrients absorbed by the roots to the leaves
Leaf structures clipart 20 free Cliparts Download images on
The Seed Classification of Flowering Plants Anatomy of Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Plants Parts of a Leaf Leaves have two main parts: The leaf blade and the Stalk or the petiole. The leaf blade: It is also called the lamina. It's generally broad and flat. It is in this layer that photosynthesis occurs.

Plant leaf structure, illustration Stock Image C023/3022 Science
Certain organs that are superficially very different from the usual green leaf are formed in the same manner and are actually modified leaves; among these are the sharp spines of cacti, the needles of pines and other conifers, and the scales of an asparagus stalk or a lily bulb. Leaf function photosynthesis
Plant Leaf Structure Photograph by Carlos Clarivan Fine Art America
GCSE WJEC Structure of plants - WJEC Leaf structure Plants adapt in order to efficiently collect raw materials required for photosynthesis. These raw materials must be transported through the.

Leaf structure narrated YouTube
The midrib contains the main vein (primary vein) of the leaf as well as supportive ground tissue (collenchyma or sclerenchyma). Figure 3.4.1. 1: A typical eudicot leaf. Many leaves consist of a stalk-like petiole and a wide, flat blade (lamina). The midrib extends from the petiole to the leaf tip and contains the main vein.

Leaf Structure, Types, Functions GCSE Biology Revision
[Figure1] Epidermis covers the upper and lower surfaces of the leaf. Usually a single layer of tightly-packed cells, the epidermis mediates exchanges between the plant and its environment, limiting water loss, controlling gas exchange, transmitting sunlight for photosynthesis, and discouraging herbivores.

Anatomy of a Leaf Diagrams 101 Diagrams
Structure of a Leaf In this module, you will: learn about the structure of a leaf.Leaves come in many shapes and sizes. This video walks through the major in.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/leaf_crossection-57bf24a83df78cc16e1f29fd.jpg)
Plant Leaves and Leaf Anatomy
1. Pulvinus: ADVERTISEMENTS: In some plants, e.g., legumes, tamarind, Mimosa (Fig. 4.2-A), mango, banyan, gold- molhur etc., the leaf base becomes distinctly swollen and forms a broadened cushion-like structure, the pulvinus, (Fig. 4.2.-8). 2. Sheathing Leaf Base:

Cross Section Of Leaf Diagram Class 10 Ncert Class X Science / Cross
A leaf is a lateral, generally flattened structure born on a stem. It is divided into three parts: leaf base (Hypopodium), petiole (Mesopodium), lamina or leaf blade (Epipodium). It develops at the node and bears buds in its axil. It originates from the shoot apical meristem and is arranged in the acropetal order of the stem.

Labeled Diagram Of A Leaf hubpages
A leaf is a compromise between two conflicting evolutionary pressures. The first is to expose a maximum photosynthetic surface to sunlight; the second is to conserve water while, at the same time, providing for the exchange of gases necessary for photosynthesis. The photosynthetic cells of leaves are of a general type known as parenchyma.
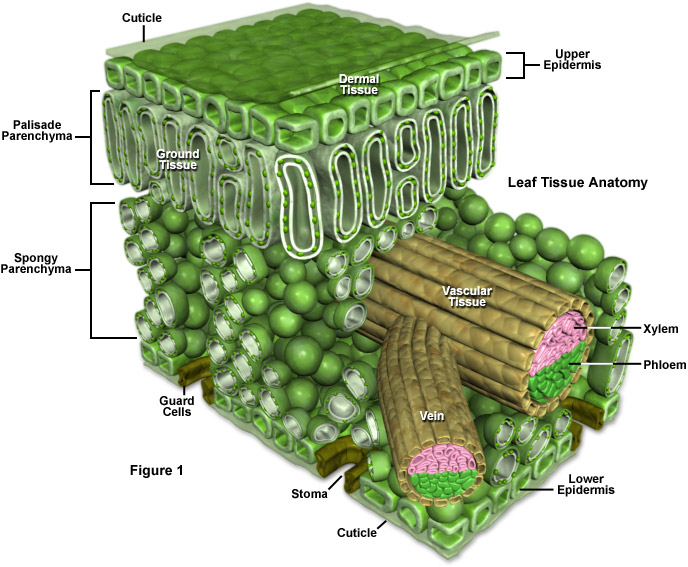
Molecular Expressions Cell Biology Plant Cell Structure Leaf Tissue
Overview By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following: Identify the parts of a typical leaf Describe the internal structure and function of a leaf Compare and contrast simple leaves and compound leaves List and describe examples of modified leaves